©
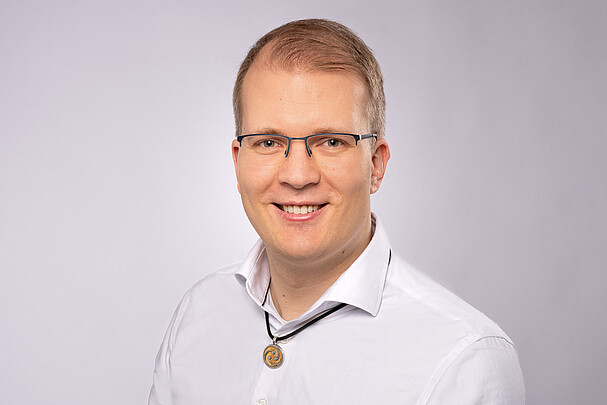
M4 Fotostudio Mirja John
©
M4 Fotostudio Mirja John
30167 Hannover

 ©
M4 Fotostudio Mirja John
©
M4 Fotostudio Mirja John
In recent years, AI achieved impressive results in different fields, incl. in computer vision, natural language processing and reinforcement learning. These breakthroughs show how AI will influence and change our daily lives, business and even research in many aspects. With the advent of deep learning and also traditional AI methods, such as AI planning, SAT solving or evolutionary algorithms, a multitude of different techniques are available these days. However, applying these techniques is challenging, and even experienced AI developers are faced with several difficult design decisions, making the development of new AI applications a tedious, error-prone and time-consuming task. Therefore, we develop new approaches to increase efficiency in AI application development by reducing the required expert knowledge, improving development time and reducing chances of error. We do this with democratization of AI and social responsibility in mind.
Research Interests
Actually, I'm interested in many topics related to AutoML, machine learning, AI and interdisciplinary applications of these. Here are some selected topics:
- Green-AutoML
- Human-centered AutoML
- Dynamic Algorithm Configuration
- Generalization of Reinforcement Learning
- Applications to production or health/medicine
Curriculum Vitae
-
Working Experience
Since 2025
Deputy Head of the Institute of AI, Leibniz UniversityApril 2023 - March 2025
Spokesperson of the Computer Science Professors, Leibniz University Hannover2022-2024
Head of the Institute of AI, Leibniz University Hannover2022
Co-Founder of the Institute for AI, Leibniz University Hannoversince 2019
Professor of Machine Learning, Leibniz University Hannover2017-2019
Lecturer (i.e., "Akademischer Rat"), University of Freiburg2014-2017
PostDoc, University of Freiburg2010-2014
Phd Student, University of Potsdam -
Education
2010-2015
Phd (Dr. rer. nat), University of Potsdam2008-2010
Master of Science, Computer Science, University of Potsdam2005-2008
Bachelor of Science, Computer Science, University of Potsdam -
Selected Awards
- 2022: ERC Starting Grant on ixAutoML
- 2020: 3rd place(*) at the official leaderboard and 1st place at the warmstart friendly leaderboard at the BBO-Challenge at NeurIPS'20 (* after fixing a minor bug)
- 2018: Winner of 2nd AutoML challenge::PAKDD2018 with aad_freibug and PoSH Auto-sklearn
- 2016: Winner of ChaLearn AutoML challenge "AutoML 5" with aad_freibug and auto-sklearn
- 2015: Winner of ICON Challenge on algorithm selection with AutoFolio (track: Par10)
- 2013: Winner of Configurable SAT Solver challenge 2013 with the Potassco team and clasp (tracks: crafted and random)
- 2012: Winner of SAT Challenge 2012 with the Potassco team and clasp (track: hard combinatorial)
- 2011: Winner of Answer Set Programming Competition with the Potassco team and claspfolio (track: NP-Problems)
- 2009: Leopold-von-Buch-Bachelor-Award (Best Bachelor in Natural Sciences 2009 at the University of Potsdam)
-
Memberships
- Co-Head AutoML.org Super Group
- Advisory board member and co-founder COSEAL.net
- L3S member of extended director board
- Member of Excellence Cluster PhoenixD
- Member and co-founder LUH Data Science Lab
- PI of KISSKI - AI Service Centre for Sensitive and Critical Infrastructures
- ELLIS Member
- CLAIRE supporter
- Partner of KI.WI - das KI-Netzwerk der Wirtschaftsregion Hannover
- Mentor at CAIMed
- Mentor at AI-Grid
- Member of Working Group 1: Technological Enablers and Data Science at Pattform Lernende Systeme
- Member of Benchmarking Network
- Member of IEEE Task Force on Automated Algorithm Design, Configuration and Selection
Previous Memberships
- Lecturer at xAIM (European Master Program on eXplainable Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Management)
-
Selected Presentations for Broader Audience
-
Industrial AI Podcast "AutoML: Did we promise ourselves too much?" (2025)
-
Ressourcenschonend und resilient: Mit KI den nachhaltigen Wandel gestalten" Panel discussion at PLS conference (Berlin; 2023, German)
-
"Was geht in dem Kopf einer KI ab?" at Medienhaus Hannover (Hannover 2023, German)
-
Künstliche Intelligenz: Science Fiction oder harte Realität? at Science Talk Phaeno (Wolfsburg; 2022, German)
-
Technische Möglichkeiten von KI zwischen Dystopie und Utopie at Ringvorlesung Deutsche Gesellschaft für wissenschaftliche Weiterbildung und Fernstudium (2021; German)
-
Automation of AI Design at TEDxFreiburg (2019; English)
Further more I gave invited talks at companies in all sizes, for example Vodafone, Bosch, Sparkasse Hannover, Hannover Re, qnips.
If you are looking for a speaker at your event, please reach out to me. For free and open events, my talks are also free of charge.
-
Publications
Zeige Ergebnisse 1 - 20 von 136